Domain Name System (DNS)
DNS resolves human-readable domain names into IP addresses. For example, www.google.com → 142.250.182.100.
Process:
- Browser checks cache
- Queries OS resolver
- Resolver checks root → TLD → Authoritative server
- IP returned and cached
HTTP / HTTPS
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Application-level protocol used for communication between clients and servers.
- HTTPS: Secured version of HTTP using SSL/TLS encryption.
Important Headers:
Content-TypeAuthorizationUser-AgentCache-Control
Curl example:curl -I https://example.com
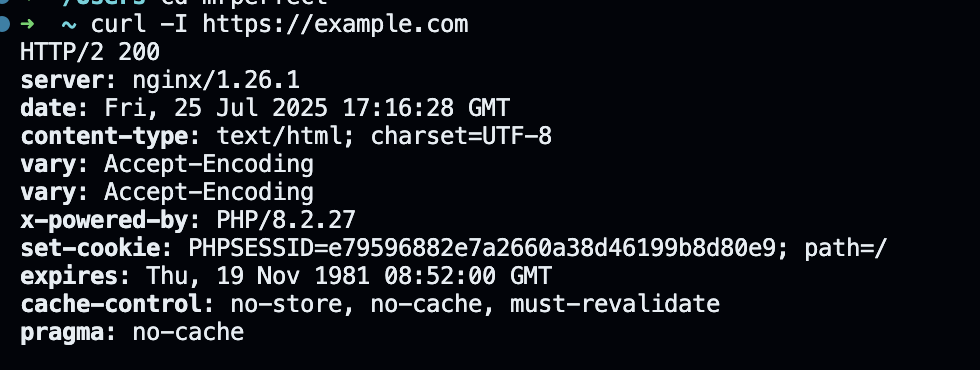
Status Codes:
- 200: OK
- 301/302: Redirect
- 403: Forbidden
- 404: Not Found
- 500: Server Error
How the Web Works
Client-Server Architecture
- Client (Browser) sends HTTP request
- Web server handles the request
- Server responds with HTML/CSS/JS
- Browser renders the content
Process:
- DNS resolution
- TCP connection (3-way handshake)
- TLS handshake (for HTTPS)
- HTTP request/response cycle
- DOM construction and rendering
Emails: Protocols and Structure
Email System Involves:
- MUA: Mail User Agent (e.g., Outlook, Thunderbird)
- MTA: Mail Transfer Agent (e.g., Postfix, Exim)
- MDA: Mail Delivery Agent (e.g., Dovecot)
Protocols:
- SMTP: Sending emails
- POP3/IMAP: Retrieving emails
Sample PHP email (using mailpit or SMTP):
mail('to@example.com', 'Subject', 'Hello World', 'From: from@example.com');
SMTP, IMAP and POP: Email Protocols
Email communication relies on different protocol to send and receive emails from one client to the other. Those protocols are as follows:
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): This protocol is used to send emails between servers and clients.
- IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): Allows email access to the email client while keeping message on the server.
- POP (Post Office Protocol): Downloads emails to a client and removed them from the server.
| Protocol | Purpose | Storage |
| SMTP | Sending emails | N/A |
| IMAP | Receiving emails and syncing emails | Emails remain on the server |
| POP | Receiving emails | Emails are removed from the server |
IMAP is preferred for accessing emails from multiple devices, whereas POP is useful for offline email access or where just a single devise is setup to receive email.
Leave a Reply